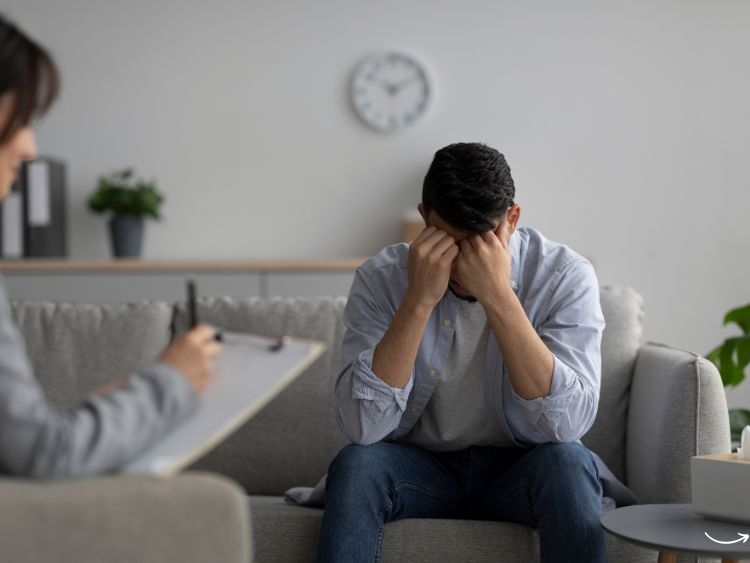
Psychotherapy has come a long way since its early days. It has evolved from mystical rituals and rudimentary methods to sophisticated, evidence-based practices. But how did we get here? Let’s take a fascinating journey through the evolution of psychotherapy, exploring its roots, pivotal moments, and modern-day practices. So, buckle up and prepare to delve into the rich history of a field that has transformed countless lives.
Ancient Beginnings
Early Healing Practices
In ancient times, mental illness was often misunderstood and attributed to supernatural forces. Shamans, priests, and healers performed rituals to expel evil spirits believed to be causing the affliction. These early attempts at psychotherapy were steeped in mysticism and lacked a scientific basis, yet they laid the groundwork for future developments.
Greek and Roman Contributions
The Greeks and Romans made significant strides in understanding the human mind. Hippocrates, often referred to as the “Father of Medicine,” proposed that mental illness resulted from imbalances in bodily fluids or “humors.” His work marked a shift from supernatural explanations to more naturalistic approaches. Additionally, philosophers like Plato and Aristotle pondered the nature of the psyche, contributing to the intellectual foundation of psychotherapy.
The Middle Ages to the Renaissance
A Return to Mysticism
During the Middle Ages, Europe saw a regression in the understanding of mental health. The influence of the Church led to a resurgence of supernatural explanations, with mental illness often seen as a sign of demonic possession. Treatments during this time were harsh and punitive, including exorcisms and confinement.
The Dawn of Humanism
The Renaissance brought a renewed interest in the human experience, including mental health. Thinkers like Johann Weyer challenged the notion of witchcraft and advocated for more humane treatment of the mentally ill. This period marked the beginning of a slow but steady shift towards more compassionate and rational approaches.
The Birth of Modern Psychotherapy
The 19th Century: Laying the Groundwork
The 19th century was a pivotal time for psychotherapy. Sigmund Freud, a neurologist, introduced psychoanalysis, which emphasized the role of unconscious processes in shaping behavior. Freud’s theories and methods, such as free association and dream analysis, revolutionized the field and laid the foundation for many contemporary practices.
The Rise of Various Schools
Following Freud, numerous schools of thought emerged, each offering unique perspectives on mental health and therapy. Carl Jung developed analytical psychology, emphasizing the collective unconscious and archetypes. Meanwhile, Alfred Adler introduced individual psychology, focusing on feelings of inferiority and the drive for self-improvement.
The 20th Century: A Boom in Approaches
Behaviorism
In the early 20th century, behaviorism emerged as a dominant force. Pioneered by figures like John Watson and B.F. Skinner, behaviorism focused on observable behaviors and their modification through reinforcement and punishment. This approach was particularly effective in treating phobias and other anxiety disorders.
Humanistic and Existential Therapies
The mid-20th century saw the rise of humanistic and existential therapies. Carl Rogers developed client-centered therapy, which emphasized the importance of empathy, unconditional positive regard, and the therapeutic relationship. Existential therapists like Viktor Frankl and Rollo May focused on issues of meaning, choice, and self-determination.
Cognitive and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies
The late 20th century brought cognitive and cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT) to the forefront. Aaron Beck’s cognitive therapy and Albert Ellis’s rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT) highlighted the role of distorted thinking patterns in mental health issues. CBT’s structured, goal-oriented approach proved highly effective for a range of disorders, including depression and anxiety.
Contemporary Psychotherapy
Integration and Eclecticism
Today, many therapists adopt an integrative or eclectic approach, combining elements from various therapeutic models to tailor treatment to individual clients. This flexibility allows for more personalized and effective interventions.
Evidence-Based Practice
Modern psychotherapy places a strong emphasis on evidence-based practice, ensuring that interventions are grounded in scientific research. This approach enhances the credibility and effectiveness of psychotherapy, providing clients with treatments that have been rigorously tested and validated.
The Role of Technology
Technology has also transformed psychotherapy. Online therapy platforms, telehealth, and mental health apps have made therapy more accessible than ever. These innovations offer new ways to deliver support and expand the reach of mental health services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary focus of psychoanalysis?
Psychoanalysis, founded by Sigmund Freud, primarily focuses on exploring unconscious processes and how they influence behavior. Techniques like free association and dream analysis are used to uncover hidden thoughts and feelings.
How does cognitive-behavioral therapy differ from other approaches?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) differs from other approaches by emphasizing the role of thoughts in influencing emotions and behaviors. CBT is structured, goal-oriented, and focuses on changing negative thought patterns to improve mental health.
What are the benefits of online therapy?
Online therapy offers several benefits, including increased accessibility, convenience, and flexibility. It allows individuals to receive support from the comfort of their own homes and can be particularly beneficial for those with mobility issues or living in remote areas.
Can different therapeutic approaches be combined?
Yes, many therapists use an integrative or eclectic approach, combining elements from various therapeutic models to best meet the needs of their clients. This flexibility allows for more tailored and effective interventions.
Summary
The evolution of psychotherapy is a testament to human ingenuity and our enduring quest to understand the mind. From ancient rituals to cutting-edge technology, the field has transformed dramatically over the centuries. Today, psychotherapy is a diverse and dynamic discipline, offering a wide range of evidence-based approaches to support mental health and well-being. As we continue to learn and innovate, the future of psychotherapy promises to be even more exciting and impactful.
Authoritative Links
- National Institute of Mental Health: https://www.nimh.nih.gov
- American Psychological Association: https://www.apa.org
- World Health Organization: https://www.who.int
- National Alliance on Mental Illness: https://www.nami.org
- Mayo Clinic – Mental Health: https://www.mayoclinic.org
By understanding the rich history and evolution of psychotherapy, we can appreciate the progress made and the potential for future advancements in this vital field. Whether through traditional methods or modern innovations, the goal remains the same: to support and enhance mental health for all.